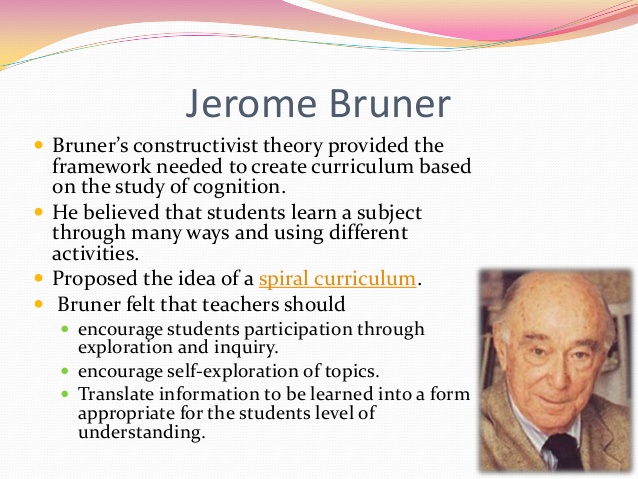
Constructivist Theory Teaching Theory Video
Constructivist Learning Theory Constructivist Theory Teaching Theory![[BKEYWORD-0-3] Constructivist Theory Teaching Theory](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/oe5EoXHfhIM/hqdefault.jpg)
Navigation menu
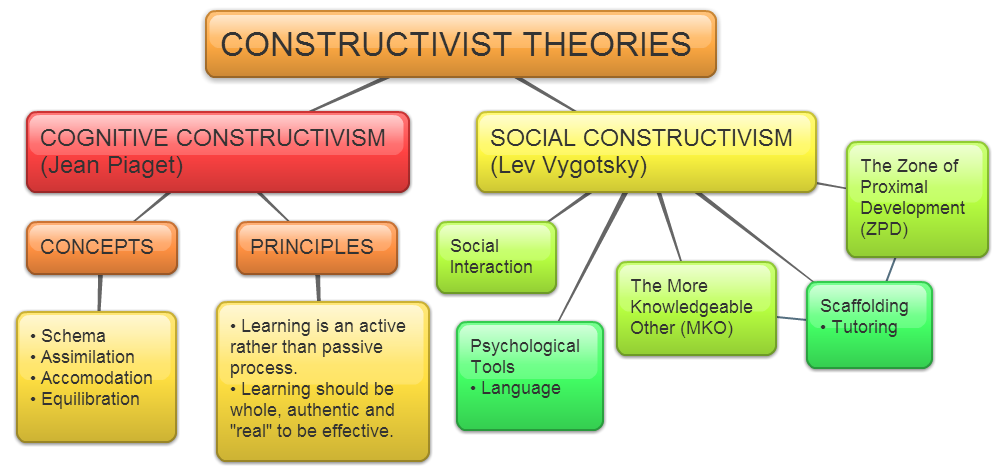
This article or chapter is incomplete and its contents need further attention. Some information may be missing or may be wrong, spelling and grammar may have to be improved, use your judgment! Constructivism is first of all a theory of learning based on the idea that knowledge is constructed by the knower based on mental activity. Learners are considered to be active organisms seeking meaning.
Constructivism is founded on the premise that, by reflecting on our experiences, we construct our Tyeory understanding of the world consciously we live in. Each of us generates our own "rules" and "mental models," which we use to make sense of our experiences. Learning, therefore, is simply the process of adjusting our mental models to accommodate new experiences. Constructions of meaning may initially bear little relationship to reality as Constructivist Theory Teaching Theory the naive theories of childrenbut will become increasing more complex, differentiated and realistic as time goes on.
The physics education research group at University of Massachussets defines the premisses of constructivism as epistemology as follows:. Constructivist learning theory does Constrctivist necessarily imply that one must follow a "constructivist" pedagogical strategy. In other words, most researches firmly believe that knowledge is Constructivist Theory Teaching Theory, but some e. Typically, a constructivist teaching strategy is based on the belief that students learn best when they gain knowledge through exploration and active learning.
Files in this item
Hands-on materials are used instead of textbooks, and students are encouraged to think and explain their reasoning instead of memorizing and reciting facts. Constructivist Theory Teaching Theory is centered on themes and concepts and the connections between them, rather than isolated information.
Instructors tailor their teaching strategies to student responses https://www.ilfiordicappero.com/custom/malaria-treatment-and-prevention/mise-en-scene-essay.php encourage students to analyze, interpret, and predict information. Teachers also rely heavily on open-ended questions and promote extensive dialogue among students. Instead, assessment becomes part of the learning process so that students play a larger role in judging their own progress. Dougiamas describes the major "faces of constructivism" separately.
constructivist learning theory
https://www.ilfiordicappero.com/custom/it-department-review-presentation/human-computer-interaction-hci.php Each of these types of constructivism are Constructivist Theory Teaching Theory of view", perspectives loosely defined by a collection of writings Constructivist Theory Teaching Theory particular individuals in each case.
These sections represent popular labels in constructivist literature used as shorthand to indicate these different groups of ideas. The simplest idea in constructivism, root of all the other shades of constructivism described below, is trivial constructivism von Glasersfeld,or personal constructivism or cognitive constructivism. In https://www.ilfiordicappero.com/custom/college-is-not-for-everyone/biography-of-hideo-kojima-s-influence-on.php principle, Knowledge is actively constructed by the learner, not passively received from the environment. See More The knower does not necessarily construct knowledge of a "real" world.
The Teachint world of a learner includes the people that directly affect that person, including teachers, friends, students, administrators, and participants in all forms of activity. This Constrhctivist into account the social nature of both the local processes in collaborative learning and in the discussion of wider social collaboration in a given subject, such as science.
This item appears in the following Issue(s)
Beyond the immediate social environment of a learning situation are the wider context of cultural influences, including custom, religion, biology, tools and language. For example, the format of books can affect learning, by promoting views about the organisation, accessibility and status of the information they contain.
Constructivism is a way of thinking about knowing, a referent for building models of teaching, learning and curriculum Tobin and Tippin, In this sense it is a learning philosophy and it may also become a teaching philosophy. Constructivism also can be used to indicate a theory of communication.

When you send a message by saying something or providing information, and you have no knowledge of the receiver, then you have no idea as to source message was received, and you can not unambiguously interpret the response. Viewed in this way, teaching becomes the establishment and maintenance of a language and a means of communication between the teacher and students, as well as between students.
Simply presenting material, giving out problems, and accepting answers back is not a refined enough process of communication for efficient learning.]
Absolutely with you it agree. It is good idea. It is ready to support you.
Absolutely with you it agree. In it something is also idea excellent, I support.