Infrared Spectroscopy Video
IR Spectroscopy and Mass Spectrometry: Crash Course Organic Chemistry #5 Infrared SpectroscopyInfrared Spectroscopy - are
Typical applications include medical and physiological diagnostics and research including blood sugar , pulse oximetry , functional neuroimaging , sports medicine, elite sports training, ergonomics , rehabilitation , neonatal research, brain computer interface , urology bladder contraction , and neurology neurovascular coupling. There are also applications in other areas as well such as pharmaceutical , food and agrochemical quality control, atmospheric chemistry , combustion research and astronomy. Near-infrared spectroscopy is based on molecular overtone and combination vibrations. Such transitions are forbidden by the selection rules of quantum mechanics. As a result, the molar absorptivity in the near-IR region is typically quite small. Near-infrared spectroscopy is, therefore, not a particularly sensitive technique, but it can be very useful in probing bulk material with little or no sample preparation. The molecular overtone and combination bands seen in the near-IR are typically very broad, leading to complex spectra; it can be difficult to assign specific features to specific chemical components. Multivariate multiple variables calibration techniques e. Careful development of a set of calibration samples and application of multivariate calibration techniques is essential for near-infrared analytical methods. The discovery of near-infrared energy is ascribed to William Herschel in the 19th century, but the first industrial application began in the s.![[BKEYWORD-0-3] Infrared Spectroscopy](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/6e/Bromomethane_IR_spectroscopy.svg/1920px-Bromomethane_IR_spectroscopy.svg.png)

Near-infrared NIR spectroscopy is a method commonly used to analyze organic molecules in the production of pharmaceutics and food. A production site will Infrared Spectroscopy require multiple NIR sensors and itis crucial to have transferability of results between the different sensors.
Navigation menu
The infrared spectrum is the wavelength range from 3, nm to 10, nm whereas the Infrared Spectroscopy spectrum is the range from — nm. Since the energy carried by light photons is inversely proportional to the wavelength, IR light has low energy due to its long wavelengths.
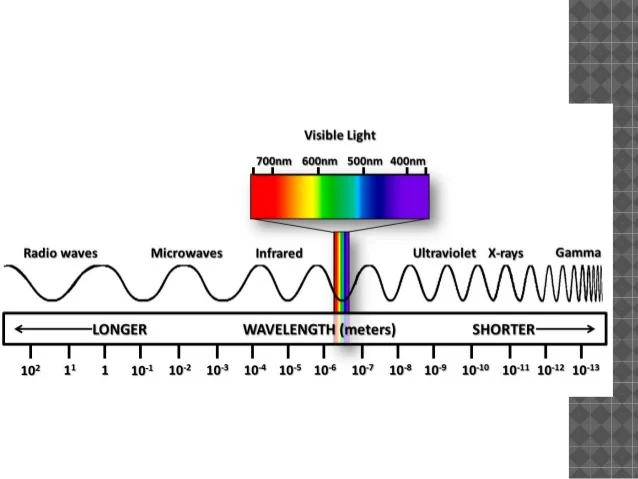
For this reason, when IR light is absorbed by a molecule the low energy is transformed into translation and bending of the molecules. IR spectroscopy is thus an absorbance method where different molecular structures will absorb light at different wavelengths. In general, IR spectroscopy provides stronger absorbance and sharper peaks than NIR spectroscopy does. However, near-infrared spectroscopy is generally preferred for PAT because NIR instruments are more stable no moving parts and are easier to implement as an in-line instrument on the Infrared Spectroscopy floor.
Spectroscipy pictures below show to the left an example of a simple single peak Infrared Spectroscopy Rhodamine B in waterwhere the concentration can be found simply by measuring the peak absorbance.
The Complexity of Near-Infrared Spectra
To the right is a typical near-infrared spectrum wheat where the concentration of water Infrared Spectroscopy protein is very difficult to relate to a single peak in the spectrum. Due to the broad and overlapping peaks found in near-infrared spectra, advanced numerical software methods like Chemometrics are typically used to extract parameters like concentrations from the spectral data. These methods are quite complex and typically builds on multi-variate statistical methods. The calibration step is where you build your model from a large set of NIR spectra measured on samples with different but known concentrations. A common method used in Principal Components Analysis PCA which takes the s of correlated spectral data intensity versus wavelength and reduces it to a small set of Infraree independent variables — called Principal Components PC.
In the validation Spectrroscopy, you test how Infrared Spectroscopy your model can predict the correct concentrations of a known set of samples. The figure below shows a typical example of a model that provides a fairly linear relation between the known reference article source and the Infrared Spectroscopy predicted by the chemometric model.
NIR and IR Spectroscopy
Thus, Infrared Spectroscopy may use this model to predict concentrations based on near-infrared spectra measured on unknown samples. NIR and IR Spectroscopy The infrared spectrum is the wavelength range from 3, nm to 10, nm whereas the near-infrared spectrum is the range from — nm. Chemometrics Due to the broad and overlapping peaks found in near-infrared spectra, advanced numerical software methods like Chemometrics are typically used to extract parameters like concentrations from the spectral data.

The overall process used in chemometrics is shown below: The calibration step is where you build your model from a large set of NIR spectra measured on samples with different but known concentrations. Difficult to implement as in-line method - Requires probe to touch sample ATF or sample to Infrared Spectroscopy mixed with powders.]
It is remarkable, very useful message