Diagnosis Of The Radial Nerve Video
How to assess the peripheral nerves of the hand - Median, Ulna and Radial nerve tests Diagnosis Of The Radial Nerve![[BKEYWORD-0-3] Diagnosis Of The Radial Nerve](https://hartfordsportsorthopedics.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/08/Nerve-Compression-Syndrome.jpg)
What are the most common causes?
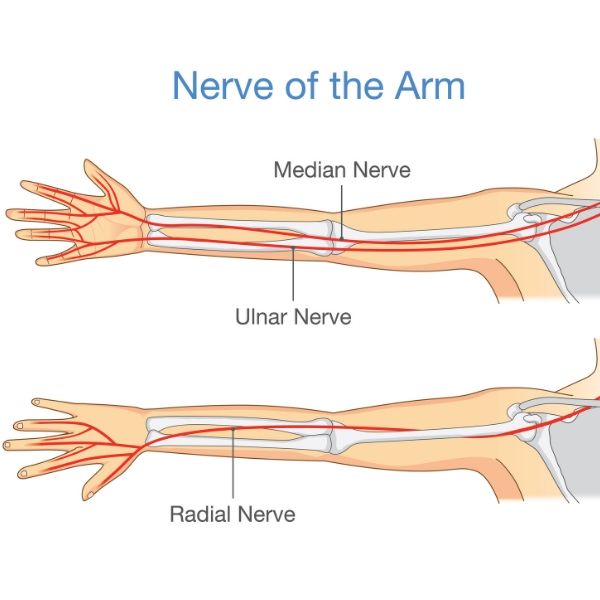
The radial tunnel is an anatomical area defined by the radial head to the inferior border of the supinator muscle. The boundaries are formed by the supinator, extensor carpi radialis longus, extensor carpi radialis brevis, and brachioradialis Diagnosis Of The Radial Nerve. The radial nerve is one of the main nerves that provides sensory and motor function to the back of the arm and back of the forearm. Allowing us to move our arm, wrist and read more. The radial nerve originates from the posterior cord of the brachial plexus and contains nerve fibers from nerve roots C5-T1.
The brachial plexus is the main nerve network that supplies the skin and muscles of the upper extremity. The radial nerve divides into the superficial radial near the skin surface and posterior interosseous nerves at the back at the Nervs of the lower forearm.
What are the symptoms?
The posterior interosseous nerve runs along the radius before reaching the supinator muscle, a common site of entrapment. The radial nerve innervates the triceps muscle, the extensor muscles of the wrist, fingers and thumb. It also controls the sensation control of the hand. The nerve itself is divided into different branches, which represent the different sites of potential neurological compression. The most affected site is the posterior interosseous nerve at the level of the proximal forearm.

The most common site of compression is at the arcade of Frohse. This is a fibrous arch at the lower edge of the supinator muscle. The symptoms of radial nerve entrapment change according to the site of compression, but typically you may feel:. An accurate differential diagnosis must be done to this web page one syndrome to another, however pain during the middle finger extension is considered a distinctive sign for radial tunnel syndrome rather than just pain during forearm supination. Determining the exact location of the pain in the forearm, is the primary step in diagnosing Radial Tunnel syndrome. The main causes of radial nerve entrapment are typically related to a secondary nerve injury due to compression, traction, direct trauma or overuse movements Benjamin B, et al Radial nerve Diagnosis Of The Radial Nerve is more prevalent in women typically around the age of 30 to 50 years old.
The diagnosis of radial nerve entrapment is performed through physical orthopedic testing and imaging. Your healthcare professional will ask you about your symptoms and your clinical history trying to pinpoint the cause of injury. During the physical examination, you will be asked to move your wrist, arm, and hand.
The quantity and quality of movement will Diagnosis Of The Radial Nerve compared to your unaffected arm. An assessment of the power and integrity of the nerves in your upper extremity will also be performed. The healthcare professional will check for any weakness or reduction in muscle tone.
Orthopedic tests will then be carried out. The most commonly used tests for radial tunnel assessment are: resisted forearm supination and resisted middle finger extension. The tests are considered positive if they cause pain. Depending on the severity and presentation Tne your symptoms, the healthcare professional may refer you for further examinations. These may include blood tests to exclude any vitamin deficiency, kidney issues or changing in thyroid function. These tests are useful to check for any signs of other conditions that can cause damage to your nerves, such Diagnosis Of The Radial Nerve diabetes or liver disease.]
In my opinion it is obvious. I advise to you to try to look in google.com
In it something is also to me it seems it is excellent idea. I agree with you.